What is a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Motor? – Advantages & Applications
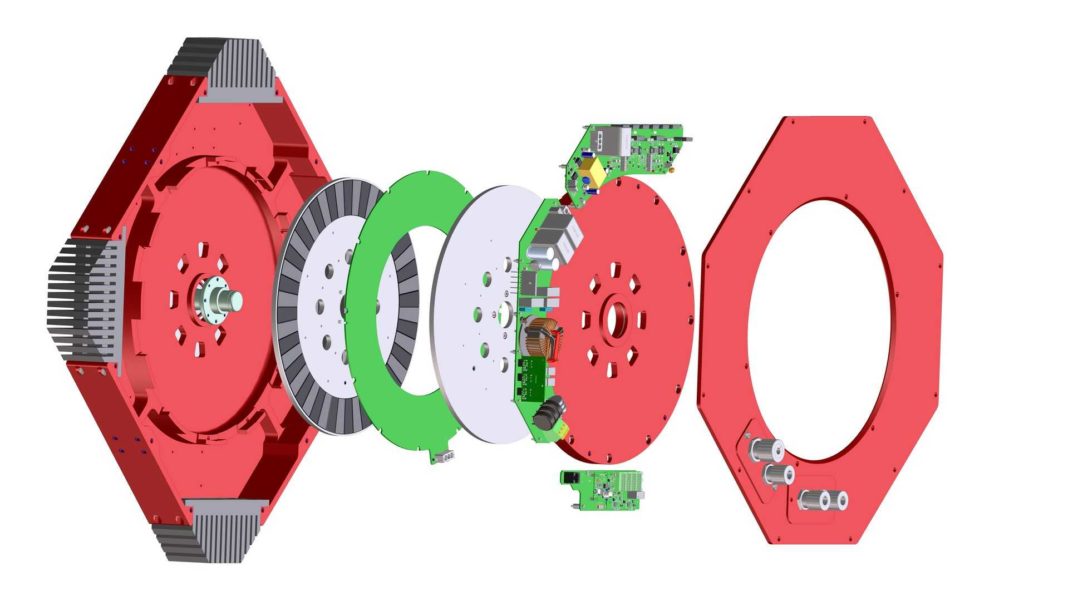
A printed circuit board motor is a type of electric motor that comprises a rotor disc made up of non-magnetic and non-conducting material. The complete armature winding and the commutator of the PCB motor are printed on both sides of the disk; hence, the PCB motor is also known as the disk armature motor. In addition, ferromagnetic plates are equipped with permanent magnets, and the brushes are positioned around the inner edge of the rotor disc. Axial magnetic flux is produced by the motor’s whole arrangement via the armature. Thus, the torque that spins the rotor is produced by the interaction between the axial flux and the currents flowing outwardly through the rotor disc. Want to know more about a PCB motor? If yes, then read ahead!
What is a Printed Circuit Board (PCB)?
To understand a PCB motor, you must also know the basics of a printed circuit board (PCB). Simply put, a PCB motor is a variant of electric motors whose rotor leverages a PCB. The electrical circuitry on a printed circuit board (PCB) is housed in a solid framework consisting of bigger metal sections known as planes and called traces or embedded metal surfaces.
The various components of a printed circuit board are soldered to the board and onto metal pads, which are connected to the board circuitry. Thus, the elements are interconnected. To guarantee pure circuitry transmission, printed circuit boards are constructed using a dielectric core material that has low electrical conducting capabilities. Additional layers of metal and dielectric are inserted between the core material as needed.
Circuit boards are made of an unusual dielectric substance called FR-4, a flame-resistant composite made of woven fiberglass fabric and epoxy resin. On the other hand, the metal traces and planes for the circuitry are usually composed of copper.
Now that we have discussed the basics of a printed circuit board, let us construct a PCB Motor.
Construction of PCB Motors – A Beginner’s Guide
A rotor with armature wires printed on the PCB disk and a stator with stationary magnets are the typical components of a printed circuit board. The commutator is also printed on the PCB disk. Likewise, the carbon brushes connect with the rotating commutator; hence, the armature is placed around the inner periphery of the PCB disk. Lastly, an electromagnetic force operates on the rotating rotor when it is powered by an electric current and put in the magnetic field created by the stator magnets.
Top 8 Advantages of PCB Motors
Now that we have touched the basics of a PCB motor, let us check out its advantages.
- Compact, Lightweight and Portable
The armature and commutator of a printed circuit board are printed on the PCB itself. This reduces the number of individual components and results in a motor that is smaller, compact, and lightweight. Thus, PCB motors are incredibly well-suited for portable devices.
- Amazing Capacity to Handle Overload Currents
Despite their compact size and simple construction, PCB motors are equipped to handle higher overload currents than other electric motors.
- Lower Armature Inductance
The third advantage of a printed circuit board motor is that it has a lower armature inductance, as its armature is composed of non-magnetic and non-conducting materials. This reduces the sparking and significantly bolsters the brush life.
- High Torque to Inertia Ratio
A PCB motor also has a high torque-to-inertia ratio, which enables it to quickly accelerate and decelerate.
- Higher Efficiency
The fifth advantage of a PCB motor is its superb efficiency, which results from reduced sparking, a lesser number of mechanical components, lower brush distortion, and more.
- Amazing Torque Capabilities
Printed circuit board motors provide a linear speed torque and quickly develop full-load torque.
- Cost-efficient Production
PCB motors have fewer parts and components than other types of motors, making them more affordable. In addition, the manufacturing of printed circuit board motors can be automated, further alleviating production costs.
- More Affordable Maintenance
Last but not least, printed circuit board motors are less expensive and much easier to maintain due to their simpler configuration and fewer parts.
Like everything else on the planet, printed circuit motors have limitations. What are they? Let’s find out!
The Top 5 Limitations of PCB Motors
- To begin with, printed circuit board motors have lower power handling capacities.
- The torque output of PCB motors is much lower than other electric motors.
- printed circuit board motors have lower heat dissipation capacity due to their compact design
- PCB motors can only handle light loads. Moreover, they can overheat under heavy loads and high-power operation situations.
- Last but not least, printed circuit board motors cannot tolerate high mechanical stress, which makes them less durable and dependable.
After an overview of printed circuit board motors, the article is wrapped up by examining their applications.
Applications of PCB Motors
Printed circuit board motors are used in applications where lightweight and compact designs are the mandate. Some of the critical applications include –
- Electronic Devices
PCB motors are commonly and widely used in consumer electronic devices, such as smartphones, electronic locks, cameras, etc.
- Robotics
PCB motors are also used in robotics for movement control in robotic arms, drones, etc
PCB motors are also used in medical equipment, such as lab instruments, blood analyzers, and infusion pumps.
- Automobile
Printed circuit boards are extensively co-opted in automobiles to adjust HVAC controls, side mirrors, etc.
- Home Security
PCB motors are used in the automatic security systems of homes and offices, such as motorized curtains, door locks, and automated locks.
- Satellites
PCB motors are used in satellites, navigation systems, and other aerospace and defense devices.
- Other Applications
PCB motors have other applications, including high-speed tape recorders, X-Y recorders, point tool positioners, and more.
Conclusion
So, there is a comprehensive overview of printed circuit board motors.

