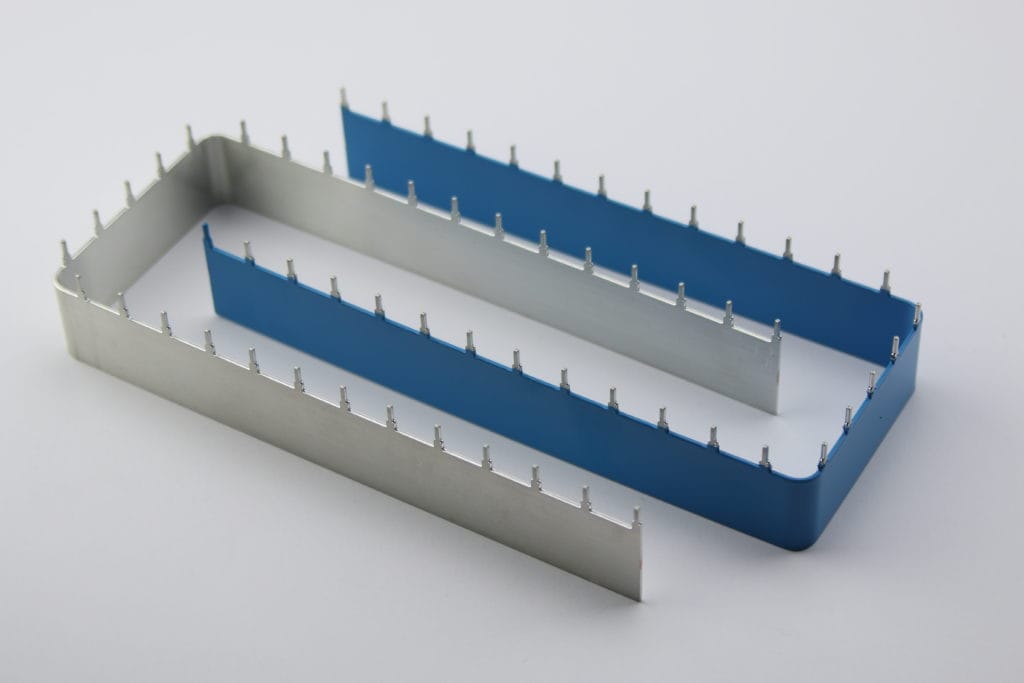
Guide to PCB Busbar and Design it on PCB
In the dynamic and ever-changing world of electronics and engineering, innovations and novelties continually drive the evolution of circuitry design. Among the many advancements, PCB busbars stand out. They have quickly emerged robust and efficient for managing power distribution in various electronic devices and systems. Sounds fascinating, right? Join us as we explore the nitty-gritty of PCB busbars, their designs, benefits, and more!
What is a PCB Busbar?
A PCB busbar is a conductive element integrated within a PCB design to distribute electrical power or signals within an electrical system efficiently. In other words, a PCB busbar is a high-current conductor that provides a stable and dependable pathway for power distribution, mitigating power losses and ensuring the efficient transmission of electricity. They are explicitly designed onto printed circuit boards to solve problems like electrical and thermal conductivity, mechanical support, and connection. Busbars serve as a centralized and low-resistance pathway to transmit electrical current to various components or subsystems within the system.
Copper or aluminum are typically the conductive materials used to make a PCB busbar. They are integrated into the layers or specific areas of the PCB during the fabrication process. Compared to copper traces, PCB busbars offer larger thickness and width and thus tolerate higher current and voltage. In addition, they also act as a support structure, owing to their rigidity and ruggedness.
The Functions of PCB Busbars – A Beginner’s Guide
The primary function of a PCB busbar is to efficiently and effectively distribute electrical signals or power within an electrical device or system. In other words, a PCB busbar is a conductive strip that facilitates electricity transmission from one point to multiple points or between different components within a system.
Some of the tangible functions of PCB busbars include –
- Power Distribution
PCB busbars serve as centralized conductive pathways that extract electrical power from a source, such as a power supply or generator, and distribute it to multiple subsystems or components within a device or system.
- Signal Distribution
Busbars carry signals within a system and route electrical signals from one point to multiple points. Thus, they facilitate communication between varying components or modules.
- Heat Dissipation
The third function of a PCB busbar is heat dissipation and thermal management. The copper or other high-conductivity materials used in PCB busbars efficiently dissipate heat generated within the electrical system, thereby contributing to power thermal management and preventing component overheating.
- Electrical Grounding
PCB busbars act as grounding conductors, offering a reliable pathway to the ground for excess or stray electrical currents and ensuring safety and protection against electrical faults.
- Space Optimization
The fifth function of a PCB busbar relates to space optimization. They facilitate a more compact and sleeker design in electronic devices by efficiently organizing and managing power distribution, freeing up space for other components or functionalities.
- High Current Handling
PCB busbars also handle high current loads, which makes them suitable for applications that need significant power distribution, such as automotive applications, power distribution systems, industrial equipment, and more.
- Flexible Configurations and Customization
Last but not least, busbars come in various shapes, sizes, and configurations, fostering customizations and personalizations for the integrated device’s electrical system.
Types of Busbars on PCB
Now, let us check out some types of PCB busbars.
- Copper PCB Busbars
Copper busbars are highly adaptable and offer excellent resistance against deprecation. Thus, they are used for large-current conductivity in high-current PCB designs, such as busway enclosures and switchgear.
- Aluminum PCB Busbars
Aluminum PCB busbars have a lower conductivity than copper busbars, yet they can withstand moderate to high currents. Aluminum busbars are lightweight and low-cost, which makes them excellent for electricity distributions in contexts with weight and cost considerations. For example, Aluminum PCB busbars are frequently leveraged in lithium batteries’ cell contact system assembly.
- Flexible Busbars
Flexible busbars are able to twist and bend without losing their electrical contact holding power. They are usually leveraged when movement, bending, and vibrations are expected.
- Multi-layer Busbars
Last but not least, multi-layer solderable PCB busbars facilitate the effective distribution of power and signals across many layers of a PCB. Electrical traces and insulating materials are stacked in many layers to create them.
Merits and Demerits of Busbars in PCBs
After a comprehensive overview of PCB busbars, let’s wrap up the article by discussing their pros and cons.
Pros of PCB Busbar
- Enhanced Strength and Excellent Rigidity
PCBs with busbars and stiffeners have excellent structural integrity. This enhanced strength enables printed circuit boards to survive in arduous situations.
- Power Distribution Optimization
The second merit of PCB busbars is that they provide a reliable bedrock for effective power distribution. In power-sensitive applications, it is crucial to keep the power supply constant, and in such a context, PCB busbars come to the rescue. They allow power and ground circuits to carry more current and maintain a stable power supply.
- Thermal Dissipation Optimization
The third and most pertinent benefit of busbars is that they improve the thermal dissipation of the PCB components and electronic products. Using PCB busbars can safeguard thermal-sensitive components from overheating.
- Bolstering Mechanical Connection
Busbars have screw nuts or holes. They enable the PCB to fix or connect with other parts by terminal blocks or screws.
Demerits of PCB Busbars
- Higher Manufacturing Complexity
When busbars are integrated into a product, the manufacturing process becomes more complicated, which results in higher production costs.
- Assembly Hurdles
Including busbars during PCB assembly is very difficult, as busbars conduct heat quickly and require higher reflow temperatures.
- Design Constraints
Busbars may limit the PCB’s architecture and component positioning, which calls for careful design considerations.
Wrapping It Up
So, there we have a crisp overview of printed circuit board busbars, their types and functions, and pros and cons.

