Fast Charging PCB : Designing PCB with Fast Charging Technology
Fast-charging PCBs are customized printed circuit boards designed to handle greater voltages and currents effectively, allowing appropriate gadgets to be charged quickly. Voltage control, communication standards, and sophisticated parts are all used to give greater electrical power while preserving device compatibility and reliability. Printed circuit boards improve energy conversion, thermal control, and security to support quicker charging rates while conforming to specific rapid charging protocols. A fast-charging PCB can also vary in design based on intended usage., i.e., whether it is to be inserted in a wired or wireless charging device.
Designing PCB with Fast Charging Technology
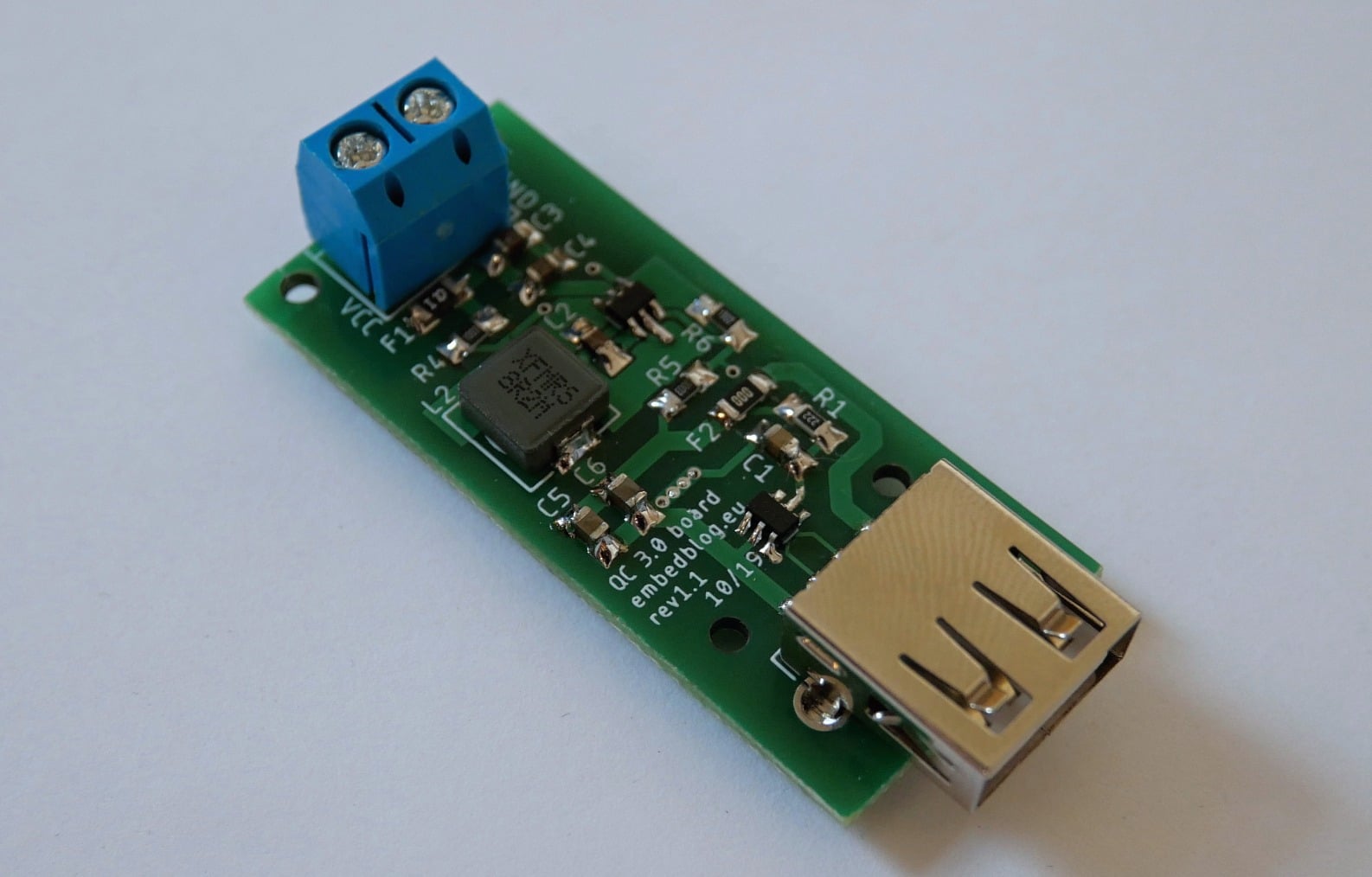
Designing a printed circuit board with fast-charging technology is an intricate procedure that requires a range of specialized equipment and a keen eye for detail. The following steps are involved in the PCB designing procedure:
- Enhanced Circuit Configuration: When designing a fast-charging PCB, create an agile and functional architecture with little signal disruption, reduced energy loss, and better thermal control capabilities. Enhance trace lengths and designs to manage greater electrical currents and guarantee reduced resistance.
- Security Characteristics: Include security measures on fast charger PCB circuit boards such as temperature surveillance, short-circuiting safeguarding, current overload safety, and excessive voltage prevention to shield the fast charger as well as all devices that are connected against possible dangers.
- Choosing Parts: Select premium parts that can withstand greater currents and higher voltages to enable lightning-fast charging. Select high-efficiency transformers, voltage controllers, diodes with substantial current ratings, and capacitors with high power densities.
- Regulating and Controlling Voltage: To ensure uniform output voltage compatible with fast charging technology, use sophisticated voltage control circuits. Control circuits guard against excessive voltage and overheating while guaranteeing the correct electricity supply.
- Heat-Dispersion Methods: To effectively disperse heat, use thermal channels, copper drips, or heat drains as part of your thermal control strategy. Ensuring the fast charger PCB circuit boards function under acceptable thermal ranges is made possible by efficient heat transfer, which avoids overheating.
- Examining and Validating: Make sure the printed circuit board layout satisfies the performance demands, security rules, and fast charging norms by thoroughly examining it via experiment, developing prototypes, and functional tests. Before implementing the concept, confirm its effectiveness, charging pace, and de aspects.
Advantages of Fast Charging PCB
Fast charging technology offers many advantages for users, making fast chargers a highly demanded product. Some of the key advantages include the following:
- Increased Charging Speeds: The main benefit is that it can power gadgets faster than regular chargers. Increased voltages and currents can be delivered via a fast-charging PCB, significantly reducing the charging duration
- Suitability for Tech Advancements: The adaptability of fast-charging technology in a PCB assures that more advanced gadgets rolling out in later years with quicker charging capacities are ready and able to work with different gadgets adopting fast-charging features.
- Increased Effectiveness: To minimize energy losses when powering up, fast-charging technology PCBs have been developed to maximize the efficacy of power conversion. Because of this increased effectiveness, recharging is more ecologically friendly as it produces less heat and uses less power.
- Practicality and Efficiency: Users may refresh their gadget’s energy reserve with the help of fast charging technology. Users needing to charge or having hectic schedules would benefit from this functionality.
- Improved Security Elements: Many fast-charging technology PCBs have sophisticated security features, including temperature tracking, shorting safeguards, overload security, and overcurrent safeguards. Providing better charging activities, such security features protect the charged device and its charger from dangers
Wireless Fast Charging Technology
Gadgets may be quickly charged using wireless fast-charging technology without conventional wiring or cables. It uses electrical induction for transmitting power via a docking station or recharging plate to an appropriate gadget. Greater intensity levels, as well as shorter charging periods, are possible due to this inventive technique, which enables gadgets to charge more quickly than with traditional charging methods.
Assuring effective power transmission and sustaining charging rates in wireless fast charging systems largely depends on the PCB configuration. Several elements must be taken into account in the printed circuit board design:
- Optimal Coil Architecture: The powering coil arrangement and structure of the electronic gadget and the recharging station should be adjusted for improved effectiveness. To optimize power transmission, the coils must be sized, aligned, and placed carefully.
- Management and Signaling Circuits: The printed circuit board has circuitry for interaction between the gadget and the charging surface to obtain the best wireless fast charging levels. Control systems optimize recharging by guaranteeing appropriate electricity supply and current management.
- Handling Heat: Because of the higher power transmission, wireless fast charging produces heat. The printed circuit board must have appropriate thermal control, including heat drains, channels, and heat transfer strategies to avoid excessive heat and preserve charging effectiveness.
- Security Procedures: Secure and dependable wireless charging of devices is ensured without endangering the health of the consumer or the gadget by the PCB’s adoption of security precautions, including monitoring of temperatures, current overload prevention, and foreign object identification.
Differences Between Fast Charging and Wireless Fast Charging
Although the common element of fast charging technology remains the same, there are particular distinctions between fast and wireless fast charging. The difference is also applicable in printed circuit board designing, making it vital to know how the two vary. The key differentiators are as follows:
Aspects of Designing:
- Fast Charging PCB: Such PCBs are designed to deal with greater currents and voltages effectively. These include security precautions, voltage control, and specialist parts to provide higher power output quickly and securely.
- Wireless Fast-Charging PCB: Improving the arrangement of the charging coils, using high-efficiency elements, controlling heat release, and combining interfaces and control circuitry are essential elements of PCB architectures in wireless rapid charging.
Effectiveness and Pace:
- Fast Charging Technology PCB: Unlike wireless alternatives, direct fast charging over wires often results in quicker charging rates since it delivers power more directly and loses less energy.
- Wireless Fast Charge PCBs: Because of the electrical losses involved in electricity transfer, wireless powering, despite being handy, often occurs at a somewhat slower pace compared to direct lightning-fast charging.
Simplicity and Interoperability:
- Fast Charging Technology PCB: Quick charging gadgets allowing direct links to cables for rapid charging are interoperable with PCBs.
- Wireless Fast Charge PCBs: Rapid wireless charge PCBs provide simplicity by eliminating the need for wired connections in gadgets supporting Qi and similar wireless power protocols.
Fast charging has become commonplace in modern gadgets because of its many benefits, primarily the capacity to save time. With all new advancements coming up with enhanced fast-charging and wireless-charging capabilities, it is time for manufacturers of PCBs to streamline their manufacturing processes for greater efficiency.

