What is the Difference Between Microstrip and Stripline in PCBs?
In Printed Circuit Boards, two kinds of transmission line structures are present in the layout. These traces are called microstrip and Stripline.
The main difference between microstrip and Stripline is their location in the PCB layout. Their placement on the electrical board is one of the ways these configurations differ from each other.
You can read this article to understand the difference between microstrip and Stripline in printed circuit board layouts.
An Introduction to Microstrips and Striplines in PCBs
The two transmission lines present in a PCB layout – microstrip line and Stripline are crucial for electronics. They guide electrical energy from one point to another and ensure efficient transmission.
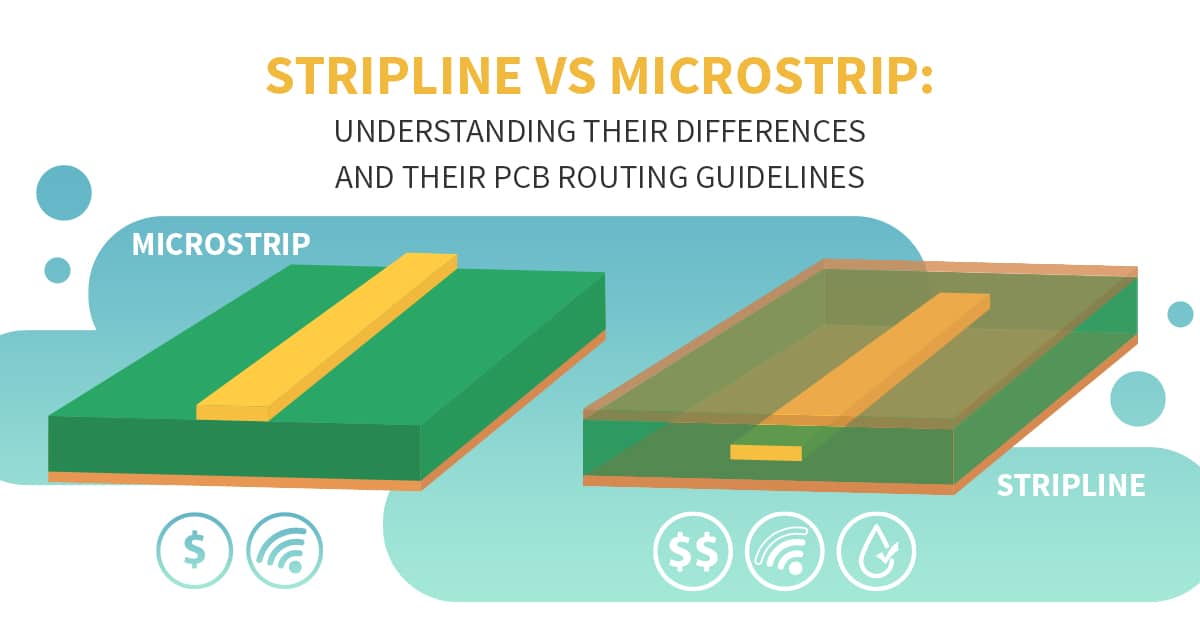
Microstrips are present on the surface layer of the circuit board layout.
Striplines are in the inner layer and sandwiched between two parallel ground planes.
It’s crucial to understand the advantages, disadvantages, and differences between Stripline vs microstrip. This information can provide insight into their applications and can help you choose the suitable one for your circuit layout designs.
Microstrips in PCBs
A microstrip line is routed on the surface of the PCB design layout. It is surrounded by two environments, which are PCB material and air.
The Advantages of Microstrips in PCBs
The advantages of microstrip transmission lines are as follows –
A microstrip line has a simple and open line structure, making connecting various electrical circuit components easier.
The simple structure makes accessing conductors for testing and modifications easier and hassle-free. It can prove helpful in the design and troubleshooting stages.
Microstrip lines can handle higher levels of power. There is better heat dissipation due to the open structure.
These transmission lines also allow for compact and efficient circuit layouts. The open structure of microstrips can prove helpful in integrating various components on the PCB layout.
The Disadvantages of Microstrips in PCBs
The disadvantages of microstrip transmission lines are as follows –
Microstrips are vulnerable to external electromagnetic interference, which is the interference of outside noises to the circuit. The open structure causes interference from the nearby components present and other external factors.
It also allows higher levels of crosstalk, and there is unwanted signal interference between transmission lines placed close to each other.
Striplines in PCBs
A stripline is routed in the inner layers of the PCB design layout. It is surrounded by a single environment, which is a PCB material.
The Advantages of Striplines in PCBs
- The advantages of stripline transmission lines are as follows –
- Striplines offer protection and act as a shield to the signal traces.
- They provide efficient isolation properties to traces placed adjacently.
- This helps reduce crosstalk when multiple transmission lines are placed together.
- These lines also help reduce electromagnetic interference, which is unwanted noise and interference. Striplines can effectively cancel out these noises that can cause interference to the electrical circuit.
- Striplines allow active and passive components to be integrated into the same layer. This leads to electrical circuit designs that are more compact and efficiently designed.
The Disadvantages of Striplines in PCBs
The disadvantages of stripline transmission lines are as follows –
- A stripline has a complex and bulky line structure. It includes two ground planes with a conductor contributing to a thicker transmission line.
- The complex structure of the striplines makes it difficult to access the conductor for testing and modifications. This makes it difficult to troubleshoot and make modifications.
- The enclosed structure of the strip lines results in poor heat dissipation. The heat generated by the signal transmissions is trapped inside and can cause thermal issues.
- Fabricating the strip lines is expensive and requires precise dimensions and materials with accurate properties. This can also increase overall manufacturing costs as they are also complex. They aren’t a cost-effective option.
The Differences Between a Microstrip and a Stripline
There are a few differences between microstrip and stripline-structured transmission lines in a printed circuit board. It can help you understand the difference between microstrip and Stripline transmission lines present in circuit boards.
Understanding the differences between a microstrip vs Stripline can help you choose the one that suits your needs for the specific requirements of the applications in the circuit boards.
The following are some of the characteristics of both the configurations used in PCBS –
- The structure of microstrip transmission lines is simple and open, whereas the structure of stripline transmission lines is complex and bulky.
- Microstrips offer better heat dissipation due to the open structure and minimize thermal issues. Striplines offer poor heat dissipation due to the enclosed structure and increase thermal issues.
- A microstrip line produces lower dielectric losses, whereas a stripline produces higher dielectric losses.
- A microstrip line also produces higher radiation losses, whereas a stripline produces lower radiation losses.
- The signal propagation is faster in microstrip lines as one side of the substrate is exposed. The signal propagation is slower as the structure is enclosed.
- The propagation constant is lower in microstrips, and the waves move faster. The propagation constant is higher in strip lines, and the waves move slower.
- In microstrips, the electromagnetic field is not fully confined. This makes them vulnerable to external interferences and some amount of radiation. In straplines, the electromagnetic field is fully confined. This lessens external interference and results in a minimal amount of radiation.
- In terms of affordability, microstrip transmission lines are cost-effective, whereas stripline transmission lines are more expensive for circuit layout applications.
The final choice between opting for Stripline vs Microstrip lies in the specific application for which you require these transmission lines. The transmission lines aren’t better than the other, and the choice depends on your specific needs for routing your PCB designs.
Conclusion
The transmission lines are necessary for PCBs, and they come with advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different kinds of applications.
You can use one of these transmission lines or both of these lines in electrical circuits. Complex circuits require a combination of microstrips and striplines for increased efficiency of the PCBs.
Also read:-

