What is LTCC Ceramic PCB and What Applications It Can Use for
The electronics and electronic components world has rapidly changed in the past few decades. A rather unique yet crucial innovation of recent times is the LTCC (Low-temperature co-fired ceramic) Printed Circuit Board (PCB). This advanced packaging technology has attracted attention in electronics due to its rare characteristics and amazing potential. Interested to know more about LTCC Ceramic PCBs? Well, read ahead!
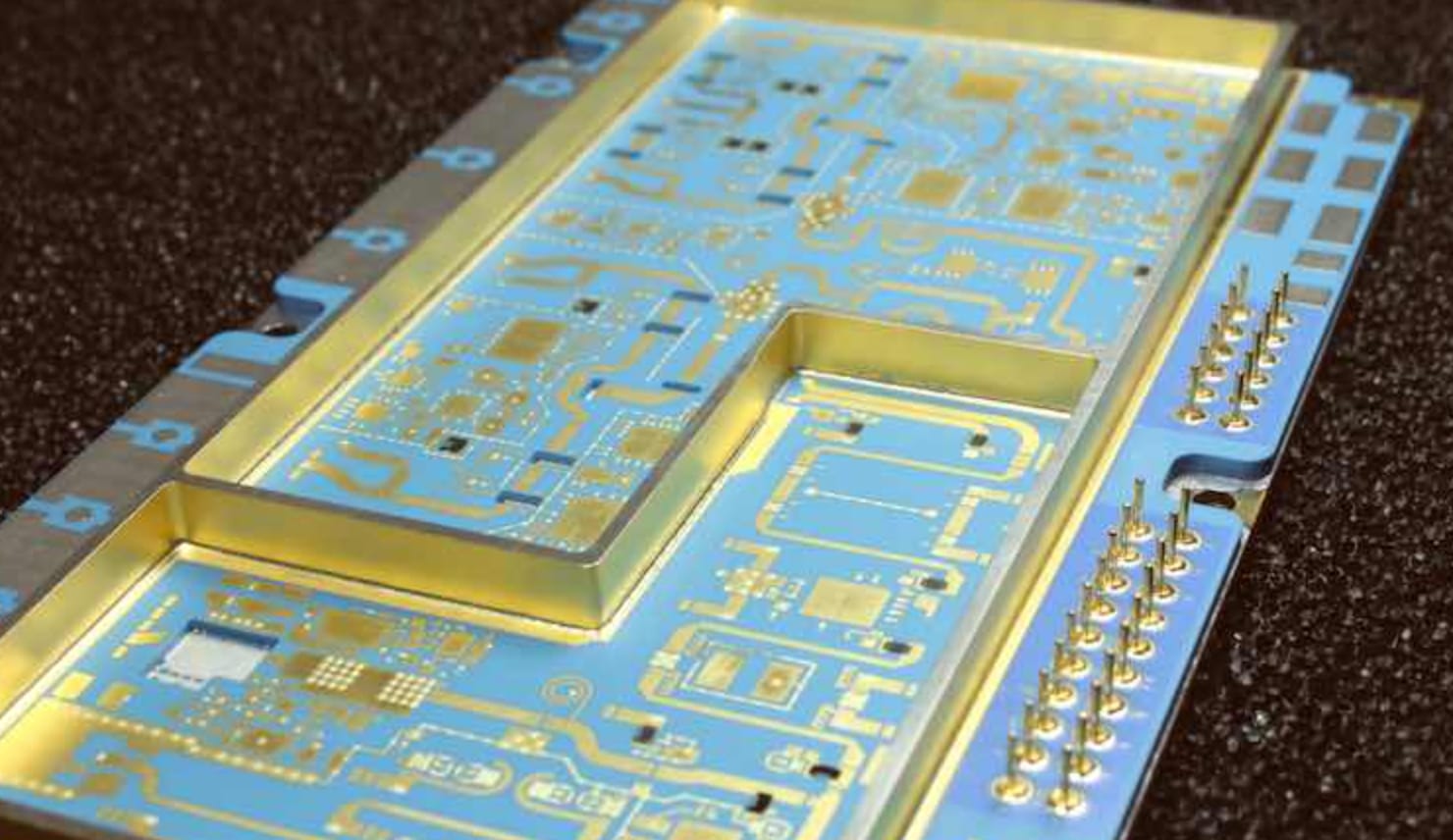
LTCC Ceramic Printed Circuit Boards
LTCC ceramic printed circuit boards are multilayered substrates composed of ceramic materials. They are co-fired (sintered) at relatively low temperatures compared to conventional ceramic processing techniques. LTCC PCB modules offer unique advantages over traditional PCBs, especially for usages that mandate high-frequency, high reliability, and harsh environment operation. Thus, they are extensively used in radio-frequency (RF), microwave-frequency, and millimeter wave frequency applications in automobile, aerospace, power, optical communication, etc.
Understandably, LTCC Ceramic PCBs are premised on LTCC technology, a specialized manufacturing mechanism developed in 1982. It helps create high-performance and highly integrated circuit boards. Furthermore, the LTCC technology is combined with the merits of ceramic materials, which include high thermal conductivity, low dielectric constant and hermetic sealing capability, and the design flexibility and multilayer prowess of printed circuit boards.
The standout features of LTCC PCBs include –
- High-frequency performance (up to millimeter-wave frequencies)
- Low dielectric loss and low signal propagation delay
- Excellent thermal conductivity
- Superb stability
- Hermetic sealing and resistance to harsh environments
- Integration of passive components like resistors, capacitors, inductors, etc
- High reliability and long operational life
Manufacturing of LTCC Ceramic PCBs
As stated, LTCC PCBs are developed using HTCC technology. It is a multilayer, low-temperature ceramic PCB manufacturing process with a sintering temperature of about 900 degrees C. During the fabrication of ceramic PCBs, the ceramic substrate is bonded with copper layers at low temperatures.
The ceramic materials for LTCC ceramic printed circuit boards include glass-ceramic, glass-plus ceramic composite, and amorphous glass materials. The amorphous glass, crystallized glass, and low melting point oxide are added to the ceramic substrate material to bolster sintering. The metal for the circuit layers is not just copper; other metals like silver, gold, and alloys can also be added.
Let us understand the manufacturing mechanism of LTCC printed circuit boards in more vivid detail.
- A ceramic belt of precise thickness is dissected into pieces of a specific width based on the incumbent requirements.
- After that, laser drilling is done on the ceramic pieces
- With the help of copper filling technology, liquid copper is injected into the silkscreen printing mechanism.
- The fourth step in manufacturing LTCC Ceramic PCBs is the precision printing of conductive paste to form the circuit images.
- Then, the passive components are placed among the circuit layers, and the PCB layers’ lamination mechanism begins.
- The three-dimensional ceramic PCB is sintered at about 900 degrees C
- Then, the masks and silkscreen are soldered on the ceramic PCB.
- The penultimate step is mounting active components via wire bonding or SMT on the LTCC ceramic PCB.
- Last but not least, a final functional test is conducted after the LTCC ceramic PCB module is completed.
Now that we know the basics of LTCC PCBs, let us check out the applications.
Applications of Low-temperature Co-fired Ceramic PCBs
LTCC ceramic technology can fabricate multilayer ceramic printed circuit boards in three-dimensional designs. Thus, the culmination is high-density circuits with a delicate trace space or width and reduced product size. LTCC ceramic PCBs have a low dielectric constant, good conductivity, and low dielectric loss. They are appropriate for RF, microwave, and millimeter-wave devices.
Some of the applications of low-temperature co-fired ceramic PCBs are –
- Automobile Electronics
LTCC ceramic PCBs are used in various automotive sensors, such as pressure, voltage, and radar sensors. They are also used for the inverter, ignition coils, water pump, and oil pump. Furthermore, electric vehicles’ air conditioning systems also co-opt LTCC PCBs.
- Electronics Communications
LTCC ceramic PCBs are also appropriate for communication devices. They are used in Bluetooth modules, transmitter or receiver modules, centralized parameter circulators, smartphone front-end modules, antenna switch modules, and power amplifier modules.
- Custom Electronic Component Fabrication
Thirdly, LTCC ceramic PCBs enable the embedding of passive components. Hence, they are widely used to customize capacitors, ceramic resistors, filters, resistors, Fantennas, baluns, couplers, power splitters, duplexes, and standard-mode chokes.
LTCC PCBs’ biocompatibility and hermetic packaging make them useful for implantable medical devices, such as cochlear implants, pacemakers, biosensors, and more.
- Optoelectronics
LTCC PCBs are also leveraged in optoelectronic applications, such as fiber optic transceivers, optical interconnects, and photogenic integrated circuits.
- Other Applications
Lastly, LTCC is a low-cost packaging technology that enables the end product to be thinner, smaller, and lighter. Hence, LTCC ceramic PCBs are frequently used for red wine shelves, hair removal devices, car refrigerators, facial cleaners for beauty, and more.
LTCC Ceramic PCBs Versus HTCC Ceramic PCBs
After a comprehensive summary of low-temperature co-fired ceramic PCBs, let us wrap up the article by checking out the difference between LTCC ceramic PCBs and HTCC ceramic PCBs.
- LTCC PCBs require sintering temperatures between 800 and 950 degrees C. HTCC ceramic PCBs need sintering temperatures between 1650 and 1850 degrees C.
- LTCC ceramic materials include glass-ceramic, glass and ceramic composite, and amorphous glass. Conversely, high-temperature co-fired ceramic PCBs’ ceramic materials include aluminum nitride, aluminum oxide, or mullite without glass.
- LTCC ceramic printed circuit boards have high speed, high wiring density, and low dielectric loss. They are the most popular PCBs for passive integration circuits and are leveraged for high-frequency and high-speed circuits. Conversely, HTCC ceramic PCBs boast superb structural strength, high thermal conductivity, excellent chemical stability, and high wiring density. These traits make HTCC PCBs a great option for high-power micro-assembled circuits, automotive high-power circuits, etc.

