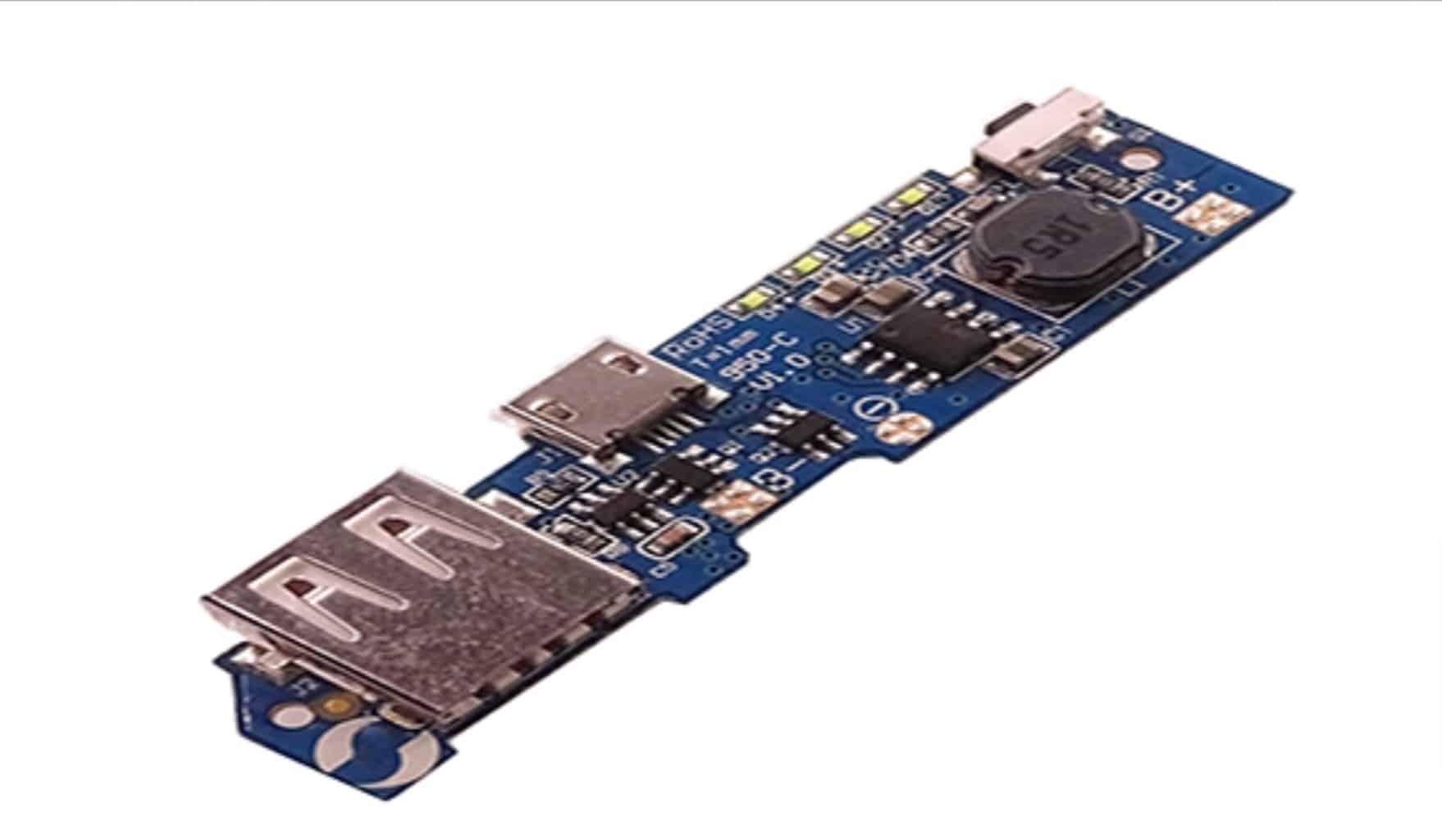
Why should you get a Mobile Charger PCB?
The printed circuit boards designed for a mobile charger are customized to transform alternate current from an electrical source into direct current, which is appropriate for powering handheld devices like tablets and cellphones. To control the degree of voltage, guarantee a consistent output, and prevent the connected gadget from excessive charging, shorting, or fluctuations in voltage, it incorporates several different elements, including converters, rectifier devices, voltage managing elements, and protective circuitry. Smartphone charging is made secure and consistent by compact dimensions, efficient energy transfer, and heat regulation of the charger’s PCB architecture.
Critical Role of Mobile Charger PCB
A properly functioning mobile charger ensures a device runs without problems. For this, having an accurately constructed mobile charger circuit board is essential. This helps prevent problems such as mobile overcharging, short-circuiting, and other issues from occurring in mobile devices.
- Current Control and Safety: Safety features in a charger PCB include overcurrent safeguard circuitry and current constraints. Because of those elements, there is no chance of damage from shorts or overcurrent to the chargers or the gadget it is attached to.
- Security Characteristics: Sensitively integrated security safeguards that secure the gadget and its charging setting include temperature gauges, surge prevention, and sudden voltage reduction. These security measures ensure A better charging process, which reduces the danger of excessive heat, voltage fluctuations, and abrupt occurrences.
- Assurance and Durability: Chargers’ strong structure and efficient circuit boards are vital factors that enhance their dependability and longevity. Durability and reliable operation are ensured using premium printed circuit board elements, proper soldering procedures, and adhering to production guidelines.
- Stabilization and Control of Voltage: A charger PCB has voltage regulating systems to ensure a consistent output voltage appropriate for each linked gadget. Maintaining steady and secure charging voltages is made possible by voltage controllers and controlling circuitry. Because of its dependability, overvoltage situations will not harm the equipment.
- Flexibility and Efficiency: The layout of the charger PCB allows for interoperability with a wide variety of gadgets by supporting many charging protocols, including USB, USB-C, and wireless charging protocols. Additionally, these adjust to multiple input voltage ranges common across different parts of the globe.
- Small Size and Mobility: Due to the tiny physical dimensions of a mobile charger PCB, lighter, more compact adapter styles are possible. Because of its small design, chargers are more accessible for customers to take about and use when traveling.
- Transformation of Electrical Energy: The process of converting alternate current coming from an electrical outlet into the direct current needed to charge portable electronics is made more accessible by a mobile charger PCB. These printed circuit boards ensure that the power supply is adapted and transformed to meet the needs of the electronic gadget while recharging by using specific circuits and parts, including rectifier devices and converters.
- Effective Transmission of Power: The structure of the printed circuit boards affects how well electricity is transferred while charging. A more effective charging procedure is achieved by minimizing losses of power and dissipating heat and energy waste through effective trail routing, part placement, and circuit layout optimization.
- Environmental Factors to Be Considered: Power-efficient solutions are included in an improved mobile charger PCB, which complies with energy-saving regulations and lowers dormant electrical consumption while not operating. The ecological effect is reduced when sustainable methods and products are used.
Precautions for Mobile Charger PCB Manufacturer
When designing a mobile charger printed circuit board, there are several precautions that a mobile charger circuit manufacturer must undertake. The precise design and construction of these parts are essential for optimal functionality and longevity of the portable chargers and, by extension, the devices they are used to charge.
- Health and safety Circuits: Incorporate a mobile charger pcb that protects against circuit shorts, excessive voltage, current overload, and polarity reversal. When there are electric malfunctions or voltage variations, these safety features shield the charging device and any electronics attached from harm.
- Conformity with Security Guidelines: Respect for pertinent safety norms and governmental qualifications and certifications is crucial. Guaranteeing that the charging device complies with safety regulations intended for charger PCB lowers the possibility of dangerous electrical currents, excessive heat, and other possible concerns to customers and electronics.
- Security Against Fuses and Surges: Incorporate surge protection mechanisms or breakers into the mobile charger circuit board layout to guard against damages caused by unexpected voltage fluctuations and surges in electricity. When unusual electric circumstances arise, these gadgets cut off the electricity supply for a backup mechanism.
- Controlling Temperature: The charger pcb architecture must consider how to dissipate heat. Employ suitable temperature management strategies, such as heat drains, heat channels, and sufficient distances between heat-producing elements, to avert getting too hot and guarantee peak productivity when charging.
- Traceability and Record-keeping: Ensure that the printed circuit board construction, element specs, assembling directions, and protocols for testing are all thoroughly documented. This paperwork guarantees transparency regarding merchandise returns or manufacturing issues, helps with the investigation, and guides future revisions.
- Examination and Confirmation: Ensure the mobile charger PCB layout is thoroughly tested and verified. Before producing the charger in bulk, ensure it passes security checks and functions within established limits by conducting stress assessments, functional evaluations, and security conformity inspections.
- Separation and Enclosure: To avoid the risk of an electrical shock, ensure that the charger PCB input and output parts are adequately isolated. Increase user security by separating their devices from high-voltage sources using separation capacitors to achieve galvanic isolation.
- Accurate Labeling and Marks: Provide the mobile charger PCB with a prominent label that includes safety precautions, manufacturing details, input/output voltage evaluations, and orientation indicators. Labels that are easy to utilize give people direction and warnings about possible dangers and how to avoid them. Ensure that the warnings also contain information about what to do and how to handle potential issues that may arise due to improper handling.
Choice and Reliability of Parts
- Invest in premium parts from reliable vendors to manufacture mobile charger PCBs.
- Make that parts like transformers, diodes, resistors, etc., fit their intended function and have the appropriate ratings.
- For permanent performance, use elements that went through reliability examinations.
EMI and RFI Reduction: Make use of methods to reduce radio-frequency issues as well as electromagnetic disturbances. To minimize electromagnetic pollution and guarantee adherence to electromagnetic compatibility regulations, protect vulnerable mobile charger pcb parts, employ suitable anchoring strategies, and include EMI filters.
Mobile chargers are vital components without which any portable gadget is incomplete. These devices ensure that the gadgets are in prime condition to function. The PCBs installed in mobile charging devices are specialized circuits that other PCBs cannot replace. The unique elements and their specific placements play a critical role in determining the ideal functionality of the PCB. As such, great precautions must be taken during designing, planning, and manufacturing to ensure compliance with manufacturing standards.

