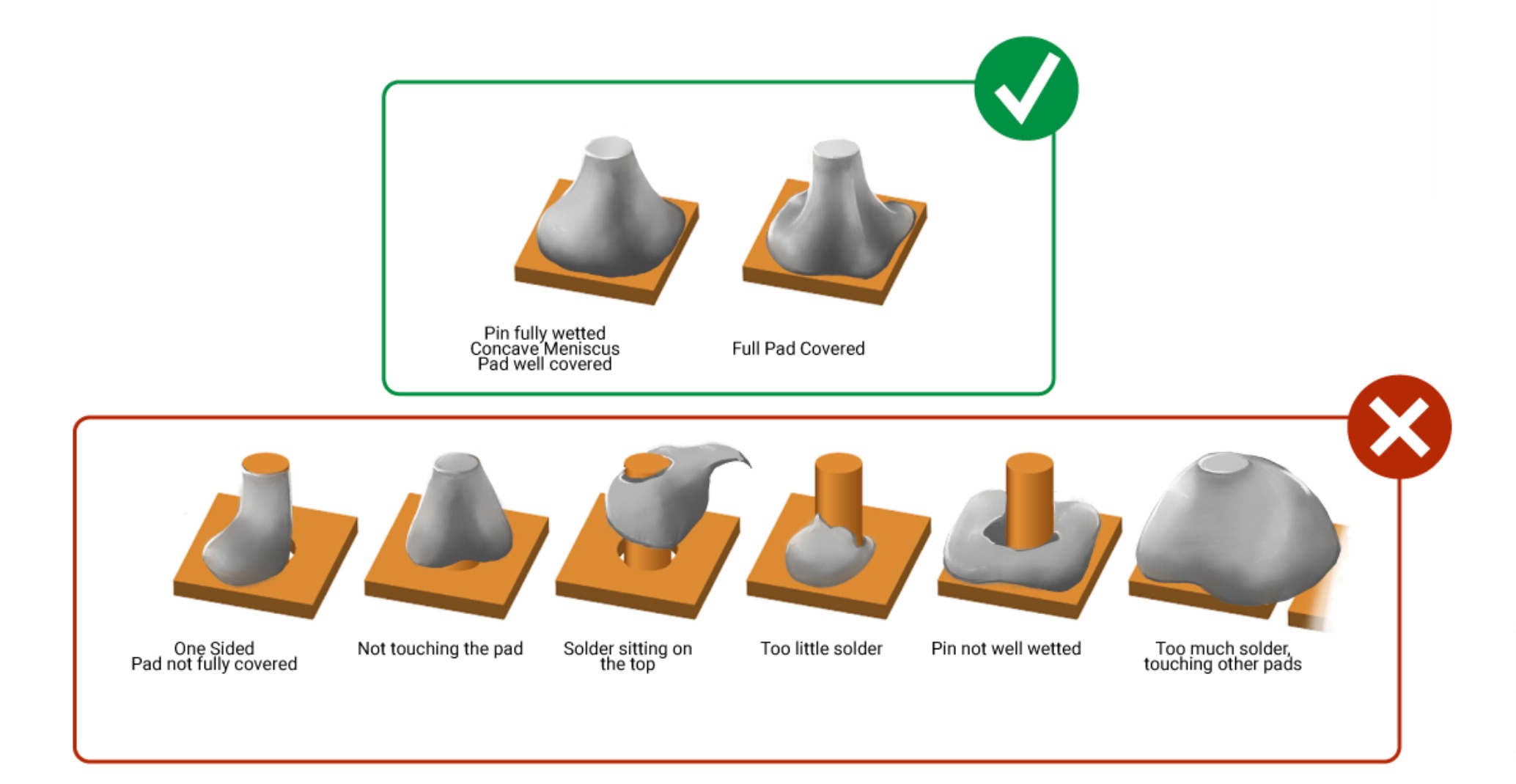
IPC J-STD-001 Standard for Soldering
Soldering is a fundamental process in the manufacture of electronic devices. It entails melting a metal alloy and using it to join two or more metal surfaces together. The quality of the soldering process directly impacts the final product’s reliability and performance.
That’s where IPC j-std-001 comes into play. IPC J-STD-001 is a widely recognized industry standard for soldering electronic assemblies. It is an IPC standard that represents acceptability criteria and process requirements. In this article, we will explore the details of IPC J-STD-001 and other aspects of j-standard soldering.
What is J-STD-001 certification?
IPC j-std-001, also known as the joint industry standard, is an industry specification for electrical or electronic assembly grouped according to the product classes. According to verification testing, manufacturability, process control regulation, and performance, electronic products are divided into three categories:
- Class 1: General electronic products
- Class 2: Service electronic products
- Class 3: high-quality electronic products
J-STD-001 A, the first version of j-standard soldering, was released in 1992. A lot has changed since then. The j-std-001H is the latest standard of j-standard solder. This standard highlights verification criteria, materials, and methods for making top-quality solder interconnections. Below are the elements that this certification includes a thorough explanation of:
- Cleaning and residue requirements
- Adhesive, coating, and encapsulation
- Equipment, material, and component
- Wire connection and terminal
- Surface mounting of the component
- Through-hole mounting
Difference between J-STD-001 and IPC-A-610
IPC-A-610 and j-std-001 are two industry standards that address the soldering and fabrication of printed circuit boards. IPC-A-610 is used for the testing of electronic assembly acceptance. Moreover, this standard provides detailed images or information about board standard procedures that ensure compliance with the operational classification.
On the other hand, j-std-001 defines soldering materials and techniques to ensure a solid solder connection and a long-lasting assembly. It also provides best practices to follow for process supervisors, engineers, and technicians.
Important requirement for soldering as per J-STD-001
There is an emphasis on some significant aspects and minor provisions in any type of standard. While speaking of soldering, it is essential to consider some essential parameters. Below are some points that you must consider while soldering with j-std-001:
- Cleaning is crucial to prevent contamination of materials, surfaces, and tools. This is because fluxes with aggressive properties can result in corrosion. As a result, the residues may attack the structural elements of the board, causing it to collapse. It may affect the lifespan of electrical components and the circuit board itself.
- Temperature control is essential for j-standard solder. It is crucial to keep the cooling and heating rates per manufacturer instructions. Thermal profiling measures numerous spots on a circuit board to determine thermal excursion during soldering. The laminated and stacked chip capacitors are used as temperature sensors to prevent thermal shocks.
- Soldiering must not harm the wire of the strand. The tinned part of the wire should be coated.
- During the forging process, a printed circuit board may have flaws that do not match the shape, fit, and functionality of the PCB assembly. It is crucial to rework or thrash this soldiering as per the customer’s wishes.
- The soldering and cleaning operations are evaluated before conformal covering and stacking are installed. Regarding PCBs, a conformal coating is a protective sheet that protects against external pollutants. It serves as the proactive covering for the printed circuit board.
- According to the design, the component lead, land pattern, solder mask, and conductor can accommodate exposed bare metal.
- AOI and AXI can be used for the visual examination of j-standard solder. A camera can automatically check for flaws and failures in the products in AOI. AXI is similar to AOI technology. It has the capability to monitor and inspect the PCB assembly after soldering. It inspects the solder connections between the components and finds numerous solder joint flaws that would otherwise go unnoticed by optical inspection tools.
The joint industry standards for space application
IPC has issued j-std-001ES for space applications. It includes uncountable steps that everyone must follow. The following are some essential steps that you must not ignore in any situation under j-std-001:
-
Corrosion
Corrosion is a crucial step in the guidelines of j-std-001. The use of silver-coated copper conductors demands a red plague control strategy, which end-users have accepted. This procedure aims to lessen the development of latent damage and cupric oxide corrosion.
-
Material
When significant aspects of the processes are restructured, validation and documentation of process adjustments should be established—solder alloys, like Sn63Pb37, are ideal for the standard. Moreover, a solder alloy that comes with good performance, reliability, and service life is acceptable.
-
Flux
There are two types of flux in j-std-001. One is resin, and another is rosin. When making changes with varied degrees of activity, testing for process compatibility is crucial. Oxidation-induced adhesive spread and solder ball development testing on the soldered part must also be conducted to successfully rule them out.
-
Thermal defense and chemical strippers
Once the soldering process is completed, chemical stripers are utilized to remove flux from the printed circuit boards. A chemical solution, paste, and cream are a few examples of chemical strippers. In theory, this cleaner has no negative impact on the material. If the component is to be soldered or changed, it must be protected against overheating and thermal stress. A thermal shunt, heat sink, and preheating are applied to achieve this. Check the heat sensitivity levels of the parts for safety, and abide by the rules.
-
Part mounting requirements
Sometimes, restrictions in the design give rise to the mounting of the component that is not capable of withstanding soldering temperature with a given process.
Components must be mounted and soldered in such cases to help attain the required temperature. It is necessary to have enough clearance between the sections of the components to perform sufficient cleaning and testing. If you want to avoid contamination, you should clean assemblies after soldering each connection.
You must remember one thing about the guidelines of j-std-001. Stress relief is given to all the leads when the material on the board is constrained. Wire attaching terminal must also receive stress relief.
-
Particulate matter assemblies
Any assemblies containing particle material must be free of all traces of soldering splashes, solder pellets, or wire clips. Solder balls can be utilized to ensure the connection’s durability if used in conjunction with a well-documented professional process.
-
Lead and wire end extensions
It is crucial to understand that wires’ ends and leads must not extend over the terminal by more than one lead diameter. Lead must be created as per the final design before assembly. The lead formation process must not damage the lead seal, connection, or wield inside the elements. Ideally, leads should be at most one lead diameter, not less than 0.8 mm or 0.031 in from the body. Remember one thing reworking the leads is not recommended for this purpose. However, you can consider minor adjustments to bend angles.
Conclusion
IPC j-std-001 is a critical standard for the production of electronic devices. It establishes the specifications and guidelines for the entire soldering process, ensuring the dependability and performance of electronic assemblies. Manufacturers can improve the overall quality of their products, reduce defects, and increase customer satisfaction by adhering to this standard.

